Introduction
Massif is MATLAB Simulink Integration Framework for Eclipse. Its purpose is to convert Simulink models to Eclipse-EMF models, and vice versa. This guide introduces the main features of the software for end-users. It also contains illustrative screenshots in order to ease the learning process and to show configuration settings.
Installation, MATLAB connectors
To install Massif follow the steps described in the install guide.
If Massif is installed you have to build connection between Massif and MATLAB. The options to do this are described in this page.
Model importing and exporting
In terms of Massif we speak about model import, when a Simulink model is converted into an EMF representation. In case of a reverse process we speak about model export. The following subsections highlight the importing and exporting capabilities of Massif.
Model import
In Massif we defined a specific EMF metamodel for describing the Simulink modeling capabilities. This Ecore representation was defined to capture the super structure of the MATLAB modeling language and thus provides a general representation for any MATLAB systems and library. The importer module is responsible to create the EMF instance model based on a single traversal on the original MATLAB representation.
How this traversal is configured is defined in the model import preferences in Window/Preferences/Simulink Preferences/Model Import Preferences.
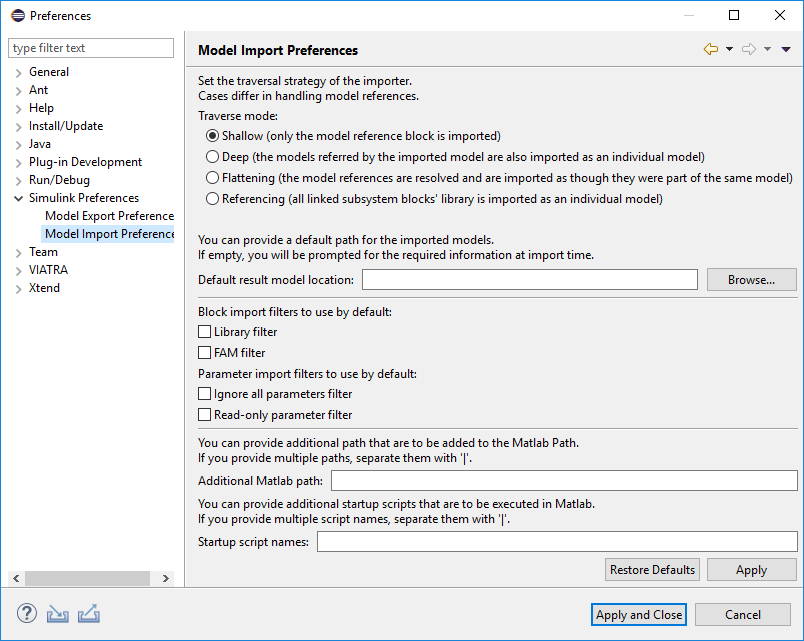
The available options are the followings:
-
Traverse mode: In Simulink there are some modeling possibilities, which make the import process complex, and can lead to unexpectedly long import times, so that these cases require extra attention. One of these is the handling of blocks called model reference blocks. These can be used to embed an individual Simulink model to another model as though it was a single SubSystem. The first three options provide different import techniques for such special model elements:
-
The Shallow mode means that when a model reference block is found, a model reference block is placed in the created EMF model, but the referenced model is not processed.
-
The Deep mode means that for each model reference block a new EMF model is created for the referenced model. Those models are saved under the same directory using the name of the referenced Simulink model.
-
The Flattening mode imports model reference blocks as though they were subsystems. This means, that the model reference is imported as a subsystem block, and the referenced model components are placed (copied) into the SubSystem.
-
In case of very large models we provide a fourth option that can significantly reduce the import time. The Referencing mode provides the following: during the import all libraries are imported only once (the first they are traversed) and whenever there is a block that has a library reference to an already imported library only a referencing subsytem is created pointing to the corresponding library.
-
-
Default result model location: This field allows the user to select a default destination path for the imported models.
-
Import filters to use by default: For further import customization there is a filtering mechanism provided by Massif in addition to the previously introduced import modes. The basic idea was to decide whether the internal part of a certain SubSystem should be represented in the imported EMF model or not. This feature is usually based a specific block parameter of the SubSystems. The folllowing filters are implemented:
-
Block import filters are working on block level:
-
Library filter: This filter allows to skip traversal of atomic library blocks inside a library model. Such blocks are not represented graphically by the tree view of the Simulink Library Browser in Matlab.
-
FAM filter: This filters all internal blocks of subsystems with
Tagparameter value ofFAM_Leaf.
-
-
Parameter import filters are working on parameters inside of blocks:
-
Ignore all parameters filter: This filter makes the importer skip all block parameters.
-
Read-only parameter filter: This filter makes the importer skip parameters that are read only.
-
-
-
Additional MATLAB Path: Folder paths given here are added to MATLAB path prior to model import. This setting allows the user to ensure that everything is available for Simulink to properly load the models and access their dependencies.
-
Startup script names: the scripts set here are executed prior to model import.
To import a model, open the context menu of an .mdl or .slx file in the package explorer within Eclipse
(right click on the file).
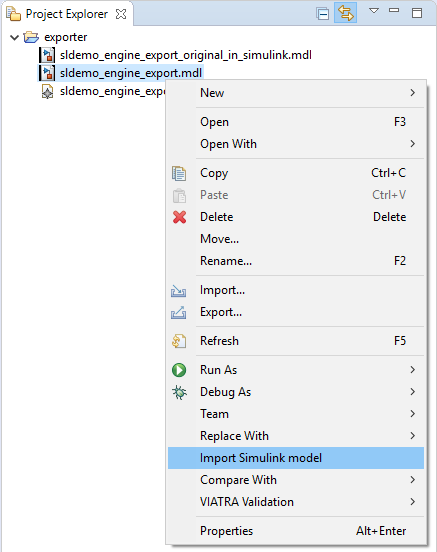
If no default path is set in preferences a popup window will appear automatically to set the required parameters.
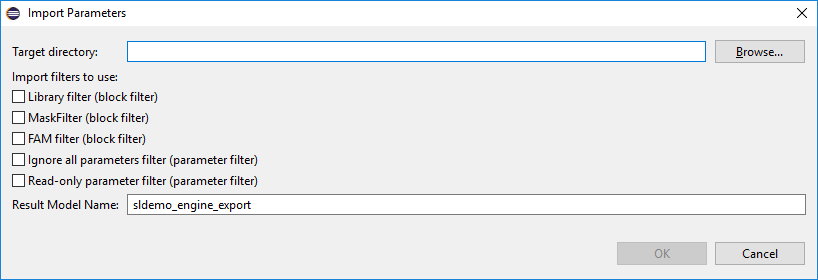
After the model is imported, a manual refresh might be needed on the destination folder to see the EMF model in the Eclipse package explorer.
Model export
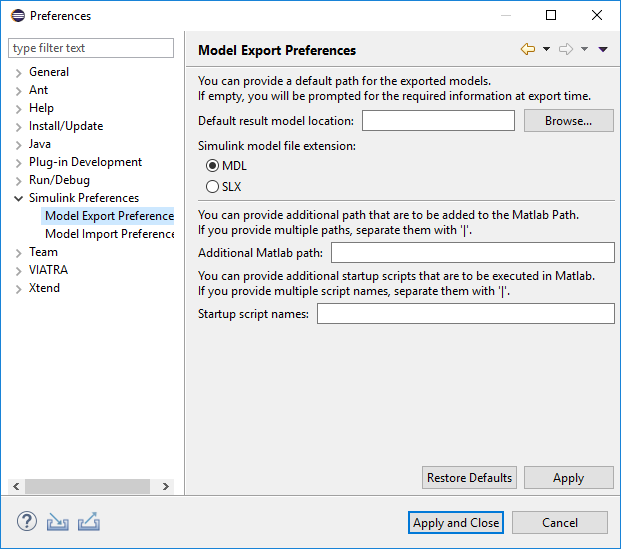
The EMF representation stores all information to build up the Simulink model using only command line model manipulation commands. This process is more simple compared to importing, thus there are only basic parameters for configuring this feature on the export preferences page.
-
Default result model location: This field allows the user to select a default destination path for the exported models.
-
Simulink model file extension: Type of the output simulink models can be
MDLorSLX. -
Additional MATLAB Path: Folder paths given here are added to MATLAB path prior to model export.
-
Startup Script names: The scripts set here are run prior to model export.
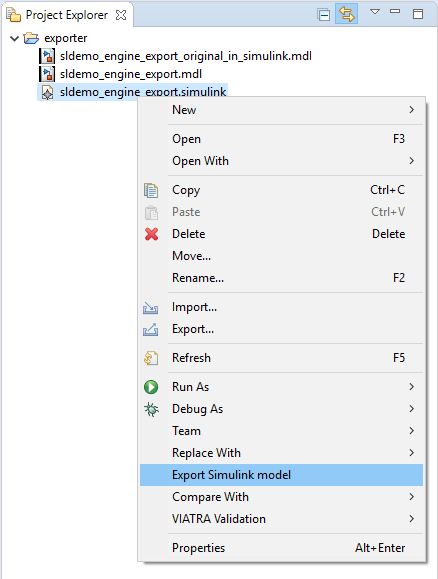
To start an export, open the context menu of a .simulink file in the package explorer (right click on the file).
The export menu entry is shown in the picture below.
If no default export path was set previously on the preferences page, a popup window will appear and the path can be selected.
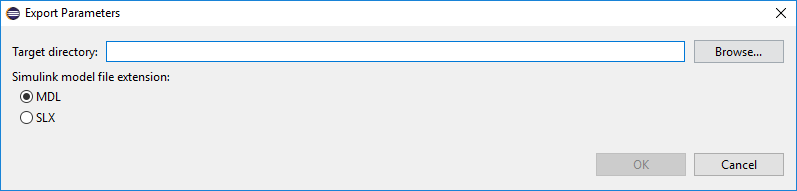
Please note that no model with the same name as the exported model should be available on the MATLAB path at the time of export. This case MATLAB would open that model and edit that, instead of creating a new one.